Azure Backup and Recovery: 7 Ultimate Strategies for Maximum Security
In today’s digital-first world, data is the lifeblood of every organization. That’s why mastering Azure Backup and Recovery isn’t just smart—it’s essential for survival, compliance, and peace of mind.
Azure Backup and Recovery: The Foundation of Cloud Resilience

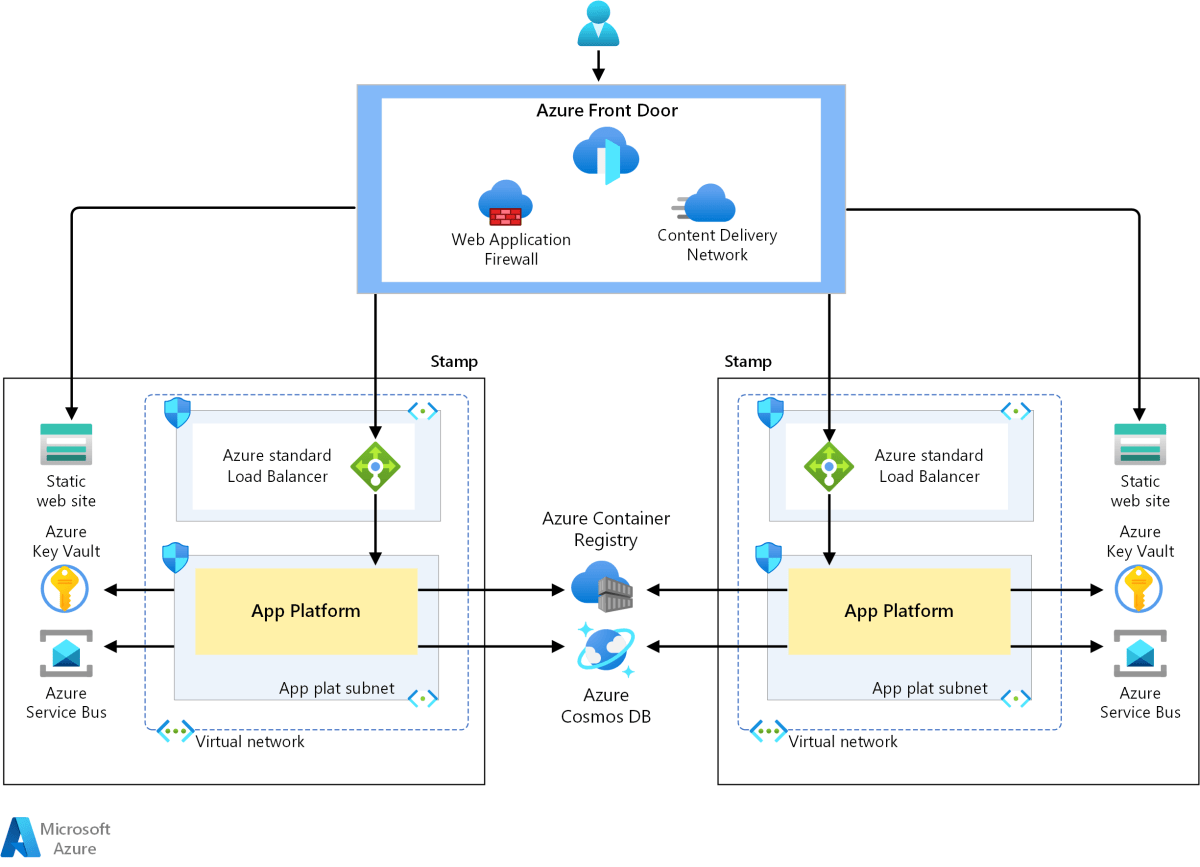
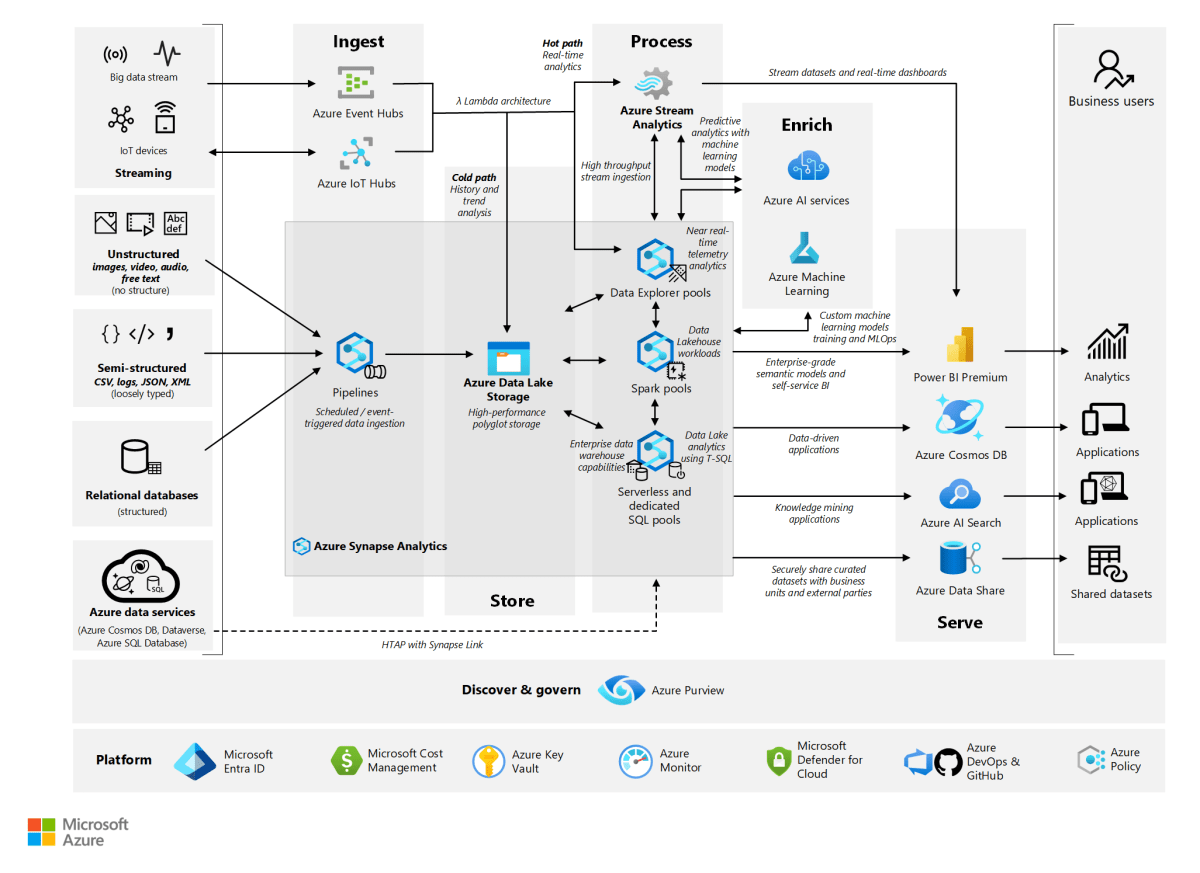
As businesses migrate to the cloud at an unprecedented pace, ensuring data durability and availability has become a top priority. Microsoft Azure provides a comprehensive suite of tools under the umbrella of Azure Backup and Recovery, designed to protect data across virtual machines, databases, applications, and on-premises systems. This integrated approach allows organizations to build a resilient infrastructure that can withstand accidental deletions, cyberattacks, hardware failures, and natural disasters.
Azure Backup and Recovery is not just about creating copies of data—it’s about ensuring business continuity. With built-in automation, policy-driven retention, and seamless integration with Azure Site Recovery, this service transforms how IT teams approach disaster recovery. Whether you’re protecting a single virtual machine or an entire hybrid data center, Azure offers scalable, secure, and cost-effective solutions.
What Is Azure Backup?
Azure Backup is a cloud-based service that enables organizations to back up and restore data from Microsoft’s global network of data centers. It eliminates the need for on-premises backup infrastructure by offering agent-based and agentless backup options for a wide range of workloads.
Key features include:
- Support for Azure Virtual Machines, on-premises servers, SQL Server, and SAP HANA
- Automated backup scheduling and retention policies
- Encryption of data at rest and in transit
- Integration with Azure Monitor for backup health tracking
By leveraging Azure Backup, companies reduce operational overhead while gaining enterprise-grade protection. You can learn more about its architecture on the official Microsoft Learn page.
What Is Azure Site Recovery?
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) complements Azure Backup by focusing on disaster recovery and business continuity. While backup is about preserving data, ASR ensures that entire systems—virtual machines, applications, and configurations—can be recovered quickly in the event of an outage.
ASR works by replicating virtual machines from on-premises environments or other clouds to Azure. In the event of a failure, these VMs can be failed over to Azure with minimal downtime. Once the primary site is restored, failback can be initiated seamlessly.
“Azure Site Recovery enables organizations to achieve recovery time objectives (RTOs) as low as 30 seconds and recovery point objectives (RPOs) under 5 minutes.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
ASR supports VMware, Hyper-V, and physical servers, making it a versatile solution for hybrid IT environments. It integrates tightly with Azure Backup to provide a complete data protection lifecycle.
Key Components of Azure Backup and Recovery
To fully leverage Azure Backup and Recovery, it’s crucial to understand its core components and how they interact. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring data integrity, availability, and rapid restoration.
Recovery Services Vault
The Recovery Services Vault is the central hub for managing backups and recovery operations in Azure. It acts as a secure container that stores backup data, replication data, and recovery points. All backup policies, monitoring, and restore operations are managed through this vault.
Important characteristics of a Recovery Services Vault include:
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS) options for long-term retention
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for security
- Support for multiple subscription and tenant scenarios
- Integration with Azure Policy for compliance enforcement
When setting up Azure Backup and Recovery, the first step is typically creating a Recovery Services Vault in your desired region. You can explore configuration options via the Azure portal.
Backup Policies and Scheduling
One of the most powerful aspects of Azure Backup and Recovery is its policy-driven automation. Backup policies define when backups occur, how long recovery points are retained, and under what conditions alerts are triggered.
A typical backup policy includes:
- Daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly backup frequencies
- Retention periods ranging from days to decades
- Instant Restore capabilities using temporary storage for faster recovery
- Long-term retention (LTR) for compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA
For example, a financial institution might configure a policy that takes hourly backups during business hours, retains daily backups for 30 days, weekly backups for 12 weeks, and monthly backups for 5 years. These policies can be applied across multiple VMs or databases simultaneously, ensuring consistency and reducing administrative burden.
Recovery Points and Restore Options
A recovery point is a snapshot of your data at a specific moment in time. Azure Backup and Recovery generates recovery points based on your backup schedule and retains them according to your policy.
When restoring data, you have several options:
- Restore to original location (e.g., same VM or database)
- Restore to alternate location (e.g., different subscription or region)
- Restore files and folders individually without restoring the entire VM
- Perform disk-level restores for granular control
The ability to restore individual files is particularly useful for scenarios like accidental deletion or ransomware attacks where only certain data is compromised. Azure also supports cross-region restore, allowing you to recover data in a different geographic location for disaster recovery purposes.
Workload-Specific Protection in Azure Backup and Recovery
Azure Backup and Recovery isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It offers tailored protection for various workloads, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. Let’s explore how it handles some of the most critical enterprise systems.
Protecting Azure Virtual Machines
Virtual Machines (VMs) are among the most commonly protected workloads in Azure. Azure Backup supports both Windows and Linux VMs with agentless backup, meaning no software installation is required on the VM itself.
The backup process works as follows:
- Azure leverages snapshot technology to capture the state of the VM’s disks
- Snapshots are transferred to the Recovery Services Vault
- Incremental backups minimize bandwidth usage and storage costs
- Backups are encrypted using Microsoft-managed or customer-managed keys
You can initiate a backup manually or rely on scheduled policies. Restoring a VM can be done in minutes, either as a full VM or by attaching recovered disks to existing VMs. This flexibility makes Azure Backup and Recovery ideal for DevOps teams and production environments alike.
Backing Up SQL Server and SAP HANA
For database workloads like SQL Server and SAP HANA, Azure offers application-consistent backups that ensure transactional integrity. This means that even if a backup occurs mid-transaction, the database can be restored to a consistent state without corruption.
Key benefits include:
- Log chain management for point-in-time recovery
- Support for Always On availability groups
- Backup compression and encryption
- Integration with SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
For SAP HANA, Azure provides native integration through the SAP HANA Backup API, enabling efficient backup and recovery of large in-memory databases. This is especially critical for enterprises running mission-critical ERP systems in the cloud.
Learn more about SQL Server backup best practices on Microsoft’s SQL documentation.
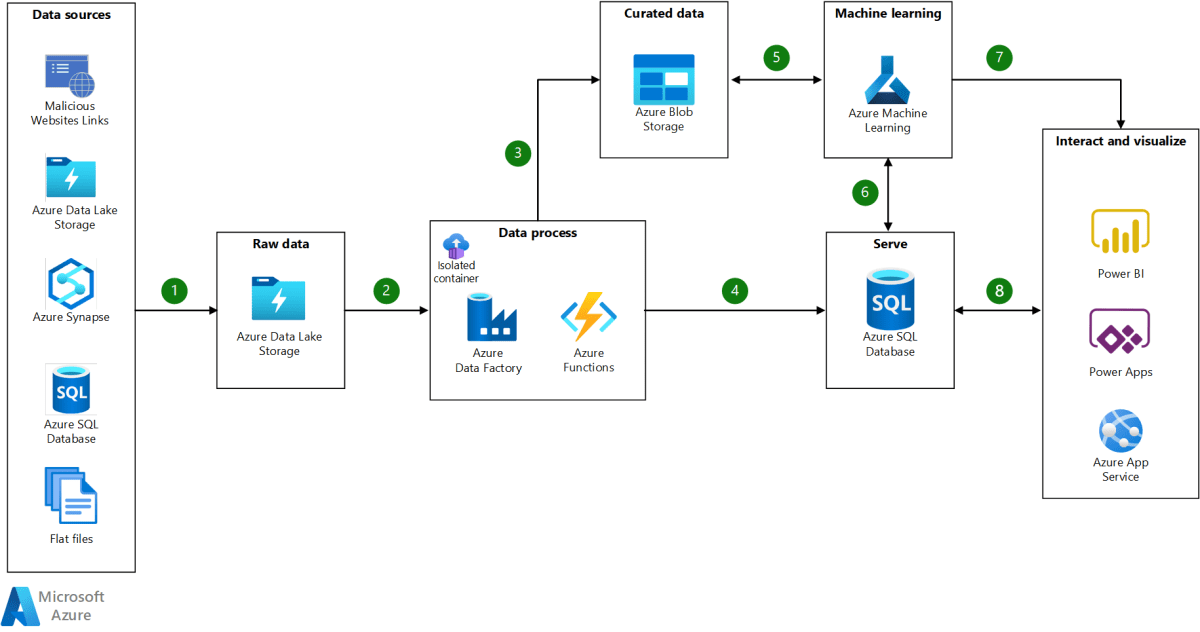
Hybrid and On-Premises Workload Support
Not all data resides in the cloud. Many organizations operate hybrid environments, and Azure Backup and Recovery excels in this space by supporting on-premises servers via the Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS) or the Azure Backup agent.
With MABS, you can back up:
- Physical servers running Windows or Linux
- Hyper-V and VMware virtual machines
- File servers, domain controllers, and application servers
Data is encrypted before transmission and stored securely in the Recovery Services Vault. Bandwidth throttling and compression help minimize network impact, making it feasible even for organizations with limited connectivity.
“Hybrid backup strategies reduce the risk of data loss by up to 90% compared to on-premises-only solutions.” — Gartner Research, 2023
This hybrid capability ensures that no system is left unprotected, regardless of its location.
Disaster Recovery with Azure Site Recovery
While Azure Backup focuses on data protection, Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is all about infrastructure resilience. Together, they form a complete Azure Backup and Recovery strategy that covers both data and system continuity.
How ASR Works: Replication and Failover
ASR continuously replicates virtual machines from a source environment (on-premises or another cloud) to Azure. This replication can be asynchronous (for lower bandwidth usage) or synchronous (for near-zero data loss).
The failover process involves:
- Stopping the primary VM (optional)
- Bringing up the replicated VM in Azure
- Reconfiguring networking and DNS to point to the new instance
- Resuming business operations with minimal downtime
Failover can be test-driven without impacting production, allowing IT teams to validate their disaster recovery plans regularly.
Failback and Reprotect
Once the primary site is restored, ASR supports a structured failback process. This includes:
- Synchronizing any changes made during the failover period
- Switching operations back to the original environment
- Reprotecting the VMs to resume replication to Azure
This reprotect step is crucial—it ensures that once failback is complete, the system is once again protected against future outages. Without reprotecting, you risk being vulnerable during the transition.
Testing Disaster Recovery Plans
One of the most overlooked aspects of disaster recovery is testing. Azure Site Recovery allows you to run non-disruptive drills that simulate a real outage without affecting your production environment.
Benefits of regular testing include:
- Validating network configurations and IP addressing
- Ensuring application dependencies are correctly mapped
- Training IT staff on recovery procedures
- Meeting compliance requirements for audit readiness
These tests generate detailed reports that highlight potential bottlenecks or misconfigurations, enabling continuous improvement of your Azure Backup and Recovery strategy.
Security and Compliance in Azure Backup and Recovery
Data protection is meaningless without robust security and compliance controls. Azure Backup and Recovery is built on Microsoft’s Trusted Cloud principles, ensuring that your data is protected from unauthorized access and meets regulatory requirements.
Encryption and Key Management
All data in Azure Backup and Recovery is encrypted by default. This includes:
- Data in transit (using TLS 1.2+)
- Data at rest (using AES-256 encryption)
- Backup storage accounts and Recovery Services Vaults
Organizations can choose between Microsoft-managed keys or bring their own keys (BYOK) using Azure Key Vault. BYOK provides greater control over encryption keys and aligns with strict regulatory frameworks.
For example, a healthcare provider handling PHI (Protected Health Information) can use customer-managed keys to ensure compliance with HIPAA requirements. This level of control is essential for industries with high data sensitivity.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Risk of insider threats is mitigated through RBAC, which allows administrators to assign granular permissions. For instance:
- Backup Operator: Can configure and manage backups but cannot delete recovery points
- Backup Reader: Can view backup status but cannot make changes
- Contributor: Full access to create and delete resources
This principle of least privilege ensures that only authorized personnel can perform sensitive operations like deleting backups or modifying policies.
Compliance and Audit Logging
Azure Backup and Recovery supports a wide range of compliance standards, including:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- ISO/IEC 27001, 27017, 27018
- SOC 1, SOC 2
- PCI DSS for payment processing environments
Audit logs are automatically generated and can be exported to Azure Monitor or Sentinel for analysis. These logs track every backup, restore, and policy change, providing a clear trail for forensic investigations or compliance audits.
Cost Optimization and Best Practices
While Azure Backup and Recovery offers powerful capabilities, improper configuration can lead to unnecessary costs. Understanding pricing models and implementing best practices is key to maximizing value.
Understanding Azure Backup Pricing
Azure Backup is priced based on:
- Amount of protected instance data (e.g., VM size)
- Backup storage used (locally redundant or geo-redundant)
- Number of recovery points retained
- Data transfer costs (minimal for same-region transfers)
Microsoft offers a tiered pricing model with different retention options. For example, short-term retention (up to 45 days) is cheaper than long-term retention (up to 99 years). Choosing the right tier based on your recovery needs can significantly reduce costs.
Use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate your monthly backup expenses before deployment.
Implementing Cost-Saving Strategies
To optimize costs in Azure Backup and Recovery:
- Use soft delete to prevent accidental deletion of recovery points (retained for 14 days by default)
- Enable backup for only critical VMs and databases
- Leverage instant restore for frequently accessed recovery points
- Archive older recovery points to lower-cost storage tiers
Archiving recovery points to Azure Archive Storage can reduce storage costs by up to 65% compared to standard backup storage. However, retrieval times are longer (up to 15 hours), so it’s best suited for compliance or infrequently accessed data.
Monitoring and Alerting
Proactive monitoring ensures that backups are running as expected and issues are caught early. Azure Monitor and Log Analytics can be used to:
- Track backup job success/failure rates
- Set up alerts for missed backups
- Generate reports on storage growth trends
- Integrate with ITSM tools like ServiceNow
For example, you can configure an alert to notify your team if a backup job fails three times in a row, allowing for rapid intervention before data is at risk.
Advanced Features and Future Trends
Azure Backup and Recovery continues to evolve with new features that enhance automation, intelligence, and integration. Staying ahead of these trends ensures your organization remains resilient in the face of emerging threats.
AI-Powered Anomaly Detection
Microsoft is integrating AI and machine learning into Azure Backup to detect unusual patterns in backup behavior. For instance, if a large number of files are deleted just before a backup, the system can flag this as a potential ransomware attack.
This proactive detection allows administrators to halt the backup chain and initiate recovery from a clean point, preventing corrupted or encrypted data from being preserved.
Integration with Azure Arc
Azure Arc extends Azure management to on-premises, multi-cloud, and edge environments. With Azure Arc-enabled servers, you can apply Azure Backup and Recovery policies uniformly across all your infrastructure, regardless of location.
This unified management plane simplifies operations and ensures consistent protection, even in complex hybrid landscapes.
Immutable Backups and Ransomware Protection
In response to the growing threat of ransomware, Azure now supports immutable backups through Azure Blob Storage’s time-based retention policies. Once a backup is written, it cannot be modified or deleted for a specified period—even by administrators with full privileges.
This feature is a game-changer for cybersecurity, as it prevents attackers from encrypting or erasing backup data to hinder recovery. Organizations in high-risk sectors like finance and healthcare are increasingly adopting immutable backups as part of their zero-trust strategy.
What is Azure Backup and Recovery?
Azure Backup and Recovery is a suite of cloud services from Microsoft that enables organizations to back up, protect, and restore data across Azure, on-premises, and hybrid environments. It includes Azure Backup for data snapshots and Azure Site Recovery for disaster recovery and VM replication.
How much does Azure Backup cost?
Costs depend on the amount of protected data, backup frequency, retention period, and storage type. Azure offers a pay-as-you-go model with no upfront costs. You can use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate expenses based on your workload.
Can I back up on-premises servers to Azure?
Yes, Azure Backup supports on-premises servers via the Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS) or the Azure Backup agent. You can back up physical and virtual machines, databases, and file servers directly to a Recovery Services Vault in Azure.
What is the difference between Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery?
Azure Backup focuses on creating point-in-time copies of data for restoration, while Azure Site Recovery is designed for disaster recovery by replicating entire virtual machines to Azure for failover during outages. They are complementary services often used together.
How do I restore a deleted virtual machine in Azure?
If soft delete is enabled, you can restore a deleted VM from a recovery point in the Recovery Services Vault. Navigate to the vault, select the VM, and choose ‘Restore VM’ from a specific recovery point. The process recreates the VM with its original disks and configurations.
Mastering Azure Backup and Recovery is no longer optional—it’s a strategic imperative. From protecting virtual machines and databases to enabling seamless disaster recovery and complying with global regulations, Azure offers a robust, scalable, and secure platform. By leveraging policy-driven automation, hybrid support, and advanced security features like immutable backups, organizations can build a resilient data protection strategy that stands up to modern threats. Whether you’re just starting your cloud journey or optimizing an existing setup, investing time in understanding Azure Backup and Recovery will pay dividends in reliability, compliance, and peace of mind.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: