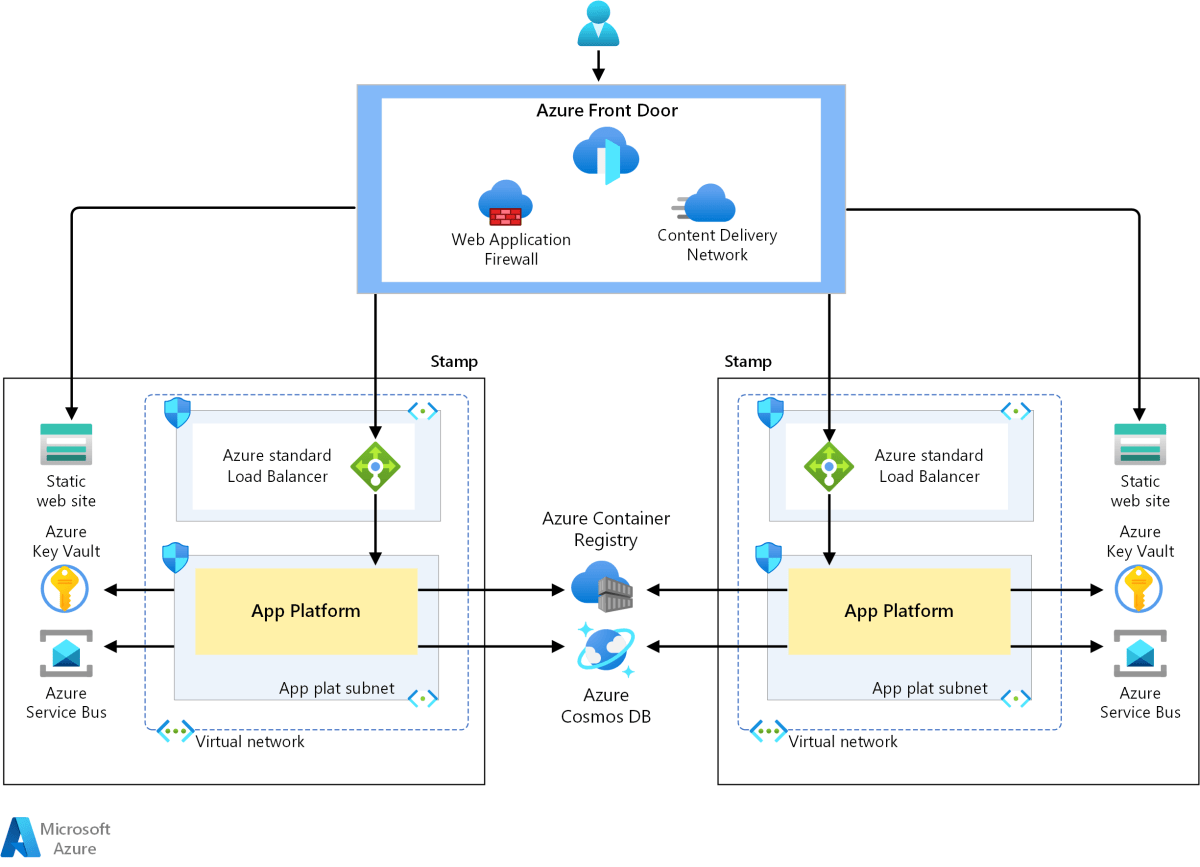
Azure Cost Management: 7 Powerful Strategies to Slash Cloud Spending
Managing cloud costs can feel like chasing shadows—especially when your Azure bills keep climbing. But with the right Azure Cost Management tactics, you can gain full visibility, optimize spending, and stop waste before it spirals out of control.
What Is Azure Cost Management and Why It Matters

Azure Cost Management is a suite of tools and practices designed to monitor, analyze, and optimize spending across Microsoft Azure environments. As organizations increasingly migrate workloads to the cloud, uncontrolled costs have become a top concern. Without proper oversight, cloud spending can quickly exceed budgets due to idle resources, over-provisioning, or lack of accountability.
Core Components of Azure Cost Management
The Azure Cost Management + Billing service, available in the Azure portal, provides native tools that help organizations track and manage their cloud expenditure. Key components include:
- Cost Analysis: A dashboard that visualizes spending trends over time, broken down by resource, service, department, or tag.
- Budgets: Customizable spending thresholds with alerts when usage approaches or exceeds limits.
- Recommendations: AI-driven suggestions for resizing, shutting down, or reserving underutilized resources.
- Exports: Automated reports that can be scheduled and delivered to storage or external systems.
These tools integrate directly with Azure subscriptions and support multi-account visibility when used with Azure Management Groups or Enterprise Agreements.
Why Azure Cost Management Is Critical for Modern IT
According to a 2023 Flexera report, organizations waste an average of 32% of their cloud spend. In Azure environments, this often stems from:
- Running virtual machines (VMs) 24/7 that are only needed during business hours.
- Storing data in premium tiers when standard or archive tiers would suffice.
- Lack of tagging policies leading to untraceable costs.
“Without cost visibility, cloud financial management is just guesswork.” — Gartner, 2023
Effective Azure Cost Management transforms cloud spending from an unpredictable expense into a strategic, measurable investment.
7 Powerful Azure Cost Management Strategies You Can’t Ignore
To truly master your Azure spending, you need more than just monitoring—you need a proactive strategy. Here are seven powerful, battle-tested approaches that leading organizations use to optimize their cloud costs.
1. Implement Detailed Tagging and Cost Allocation
Tags are key-value pairs attached to Azure resources (e.g., Department: Marketing, Environment: Dev). When used consistently, they enable granular cost tracking and accountability.
- Define a tagging policy across teams and enforce it via Azure Policy.
- Use tags to allocate costs to departments, projects, or cost centers.
- Integrate tags with Cost Analysis to generate custom reports by business unit.
For example, a retail company might tag all staging environment resources with Environment: Staging and Owner: DevOps-Team, making it easy to identify and shut down non-production workloads after hours.
2. Leverage Azure Reservations and Savings Plans
One of the most effective ways to reduce Azure costs is by committing to long-term usage through Reserved Instances (RIs) or Savings Plans.
- Virtual Machine Reservations: Save up to 72% by reserving VMs for 1 or 3 years.
- Savings Plans: Apply flexible compute savings across services like Azure Functions, App Services, and VMs.
- SQL Database Reservations: Reduce database costs by up to 57% with reserved capacity.
Microsoft recommends using the Recommendations blade in Azure Cost Management to identify reservation opportunities based on historical usage.
3. Automate Shutdown of Non-Production Resources
Development and testing environments often run 24/7 but are only used during business hours. Automating shutdowns can cut costs by 60–70%.
- Use Azure Automation or Logic Apps to start/stop VMs on a schedule.
- Leverage Azure DevTest Labs to enforce auto-shutdown policies.
- Set up alerts for resources running outside approved hours.
For instance, a financial services firm reduced its monthly Azure bill by $18,000 simply by scheduling nightly shutdowns for 120 non-critical VMs.
4. Optimize Storage Tiers and Lifecycle Policies
Storage costs can silently accumulate, especially when data is stored in high-performance tiers longer than necessary.
- Migrate infrequently accessed data from Hot to Cool or Archive blob storage tiers.
- Use Azure Blob Storage Lifecycle Management to automate tier transitions and deletions.
- Delete orphaned disks and snapshots that are no longer needed.
A media company saved over $12,000 annually by moving old video archives to the Archive tier and setting lifecycle rules to delete temporary backups after 90 days.
5. Right-Size Virtual Machines and Databases
Over-provisioning is one of the biggest sources of cloud waste. Many organizations deploy large VMs “just in case,” but usage data often shows they’re underutilized.
- Use Azure Monitor to analyze CPU, memory, and disk usage over time.
- Downsize VMs from D4 to D2 series if CPU usage averages below 20%.
- Scale down SQL databases during off-peak hours using elastic pools or auto-pause features.
The Azure Cost Management Recommendations page often flags oversized resources with estimated savings—sometimes up to 50% per resource.
6. Use Azure Advisor for Continuous Optimization
Azure Advisor is a personalized cloud consultant that analyzes your configurations and provides actionable recommendations.
- Identifies idle or underutilized resources.
- Recommends enabling backup for critical VMs (which can prevent costly data loss).
- Suggests high-availability improvements that also impact cost efficiency.
While not all recommendations are cost-related, the Cost tab focuses specifically on savings opportunities. Regularly reviewing Advisor insights keeps your environment lean and efficient.
7. Monitor Multi-Subscription and Multi-Tenant Spending
Enterprises with multiple Azure subscriptions or tenants face unique challenges in cost visibility.
- Use Azure Management Groups to aggregate subscriptions under a single governance structure.
- Enable Cross-Subscription Cost Analysis in Azure Cost Management to view consolidated spending.
- Apply budget alerts at the management group level to track organizational spend.
For organizations using Enterprise Agreements (EA), the Azure Cost Management platform supports billing scope aggregation across all enrolled subscriptions, providing a unified financial dashboard.
How to Set Up Azure Cost Management: A Step-by-Step Guide
Getting started with Azure Cost Management doesn’t require third-party tools—Microsoft provides robust native capabilities. Here’s how to set it up effectively.
Step 1: Access Azure Cost Management + Billing
Navigate to the Azure portal and search for Cost Management + Billing. From there, you can access all cost-related features.
- Ensure you have the Cost Management Reader or Contributor role to view or manage costs.
- Select the appropriate billing scope (subscription, resource group, or management group).
Step 2: Configure Cost Alerts and Budgets
Budgets are essential for proactive cost control.
- Go to Budgets and click Add.
- Set a monthly budget amount (e.g., $5,000).
- Define alert thresholds (e.g., 80% and 100% of budget).
- Specify email recipients, including distribution lists or external stakeholders.
You can also use Action Groups to trigger automated responses, such as sending a Slack message or creating a ticket in ServiceNow when a budget is exceeded.
Step 3: Run a Cost Analysis Report
The Cost Analysis tool is your financial dashboard for Azure.
- Select your billing scope and date range (last month, last quarter, etc.).
- Group data by Service Name, Resource Group, or Tag.
- Filter by specific services (e.g., Virtual Machines, Blob Storage) to drill down.
Save frequently used views as pinned charts on your Azure dashboard for quick access.
Step 4: Export Reports for Finance Teams
Finance and procurement teams often need structured data for audits or forecasting.
- Go to Exports and create a daily or monthly export.
- Choose CSV or Parquet format and specify a storage account.
- Integrate with Power BI or Excel for advanced reporting.
Exports can include detailed line-item costs, making them ideal for chargeback or showback models.
Advanced Azure Cost Management Tools and Integrations
While native Azure tools are powerful, integrating third-party solutions can enhance visibility, automation, and governance.
Azure Cost Management API for Custom Dashboards
The Azure Cost Management API allows developers to pull cost data programmatically.
- Build custom dashboards using Power BI, Grafana, or internal BI tools.
- Automate cost validation in CI/CD pipelines.
- Integrate cost checks into DevOps workflows (e.g., block deployments that exceed budget).
For example, a SaaS company uses the API to display real-time cloud costs on a wallboard in their DevOps war room, fostering cost-aware culture.
Third-Party Tools: CloudHealth, Apptio, and Azure Lighthouse
For complex environments, third-party tools offer deeper analytics and multi-cloud support.
- CloudHealth by VMware: Provides advanced cost allocation, anomaly detection, and carbon footprint tracking.
- Apptio Cloudability: Offers showback/chargeback models and integration with ERP systems.
- Azure Lighthouse: Enables managed service providers (MSPs) to manage multi-tenant cost governance at scale.
These tools often provide predictive analytics, forecasting, and benchmarking against industry peers.
Integrate with Azure Policy for Governance at Scale
Prevent cost overruns before they happen by enforcing policies.
- Create policies that require tags on all new resources.
- Block deployment of specific VM sizes in non-production subscriptions.
- Enforce use of reserved instances for production workloads.
For example, a policy can automatically deny the creation of a Standard_D8s_v3 VM in a dev subscription unless approved via an exception process.
Common Azure Cost Management Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced teams make costly errors. Here are the most common pitfalls and how to avoid them.
Mistake 1: Ignoring Orphaned Resources
When VMs are deleted, their associated disks and public IPs often remain—still incurring charges.
- Regularly audit for unattached disks and delete them.
- Use Azure Policy to auto-tag resources with creation date and owner.
- Set lifecycle rules to delete orphaned resources after 30 days.
A healthcare provider discovered $9,000 in monthly charges from 217 unattached disks—easily fixed with automation.
Mistake 2: Overlooking Data Transfer Costs
Data egress (outbound data) from Azure can be expensive, especially across regions or to the internet.
- Avoid frequent cross-region replication unless necessary.
- Use Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) to reduce egress fees.
- Compress data before transfer and cache responses.
For example, transferring 10 TB of data from Azure US East to the internet costs ~$1,250/month. Using CDN can reduce this by up to 60%.
Mistake 3: Failing to Review Reserved Instance Utilization
Buying reservations without monitoring usage can lead to wasted commitments.
- Check the Reservation Utilization report monthly.
- Exchange or refund unused reservations via the Azure portal.
- Use Scope Assignment to ensure reservations apply to the right subscriptions.
One company lost $42,000 in unused reservations because they migrated workloads to AWS but forgot to cancel their Azure RIs.
Best Practices for Sustainable Azure Cost Optimization
Cost management isn’t a one-time project—it’s an ongoing discipline. These best practices ensure long-term success.
Foster a FinOps Culture
FinOps (Cloud Financial Management) is a collaborative approach involving finance, engineering, and operations.
- Train developers to consider cost when designing architectures.
- Share cost reports with team leads to promote accountability.
- Run quarterly FinOps reviews to assess savings and set new goals.
Companies with mature FinOps practices report 30–50% lower cloud waste.
Conduct Regular Cost Audits
Schedule monthly or quarterly cost reviews to catch inefficiencies early.
- Audit all running VMs and their utilization rates.
- Review storage accounts for redundant or outdated data.
- Validate that all reservations are being fully utilized.
Use Azure’s Cost Analysis tool to generate audit-ready reports.
Leverage Azure Hybrid Benefit and BYOL
If you have existing Windows Server or SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance, you can save up to 80% using Azure Hybrid Benefit.
- Apply AHUB to VMs and Azure SQL to reduce licensing costs.
- Use License Mobility to bring your own licenses (BYOL) to Azure.
- Automate AHUB application via ARM templates or Terraform.
A manufacturing firm saved $68,000 annually by applying AHUB across 45 production VMs.
Future Trends in Azure Cost Management
As cloud environments grow more complex, Azure Cost Management is evolving to meet new challenges.
AI-Driven Cost Predictions and Anomaly Detection
Microsoft is enhancing Azure Advisor with machine learning to predict future spend and detect unusual spikes.
- Receive alerts if your daily spend suddenly jumps 200%.
- Get forecasted bills based on current usage trends.
- AI will soon recommend optimal reservation purchases automatically.
These features are already rolling out in preview and will become core to cost governance.
Carbon-Aware Cost Optimization
Sustainability is becoming a financial factor. Azure is introducing tools to optimize workloads based on carbon intensity.
- Run batch jobs when renewable energy is available.
- Choose regions with lower carbon footprints to reduce environmental and regulatory costs.
- Track your cloud carbon emissions alongside financial reports.
Cost and sustainability are converging—smart organizations will optimize both.
Integration with AI and Serverless Workloads
As AI and serverless (e.g., Azure Functions, Logic Apps) usage grows, cost models are shifting from fixed to consumption-based.
- Monitor function executions and duration to avoid runaway costs.
- Set budget alerts for AI model training jobs.
- Use Durable Functions to manage long-running processes efficiently.
Granular monitoring will be essential as micro-billing becomes more prevalent.
What is Azure Cost Management?
Azure Cost Management is a set of tools and practices offered by Microsoft to help organizations monitor, analyze, and optimize their spending on Azure cloud services. It includes features like cost analysis, budgeting, recommendations, and reporting to improve financial control over cloud resources.
How can I reduce my Azure cloud costs?
You can reduce Azure costs by using reserved instances, right-sizing resources, automating shutdowns, optimizing storage tiers, implementing tagging for accountability, and leveraging tools like Azure Advisor and Cost Management recommendations. Regular audits and a FinOps culture also contribute to sustained savings.
Are Azure reservations worth it?
Yes, Azure reservations can save up to 72% on virtual machines and up to 57% on SQL databases. They are most beneficial for stable, predictable workloads running for at least one year. However, it’s crucial to monitor utilization to avoid paying for unused capacity.
Can I track costs across multiple Azure subscriptions?
Yes, Azure Cost Management supports cross-subscription cost analysis. By using Management Groups or Enterprise Agreements, you can aggregate spending across multiple subscriptions and apply budgets and reports at scale.
What is the difference between Azure Cost Management and Azure Advisor?
Azure Cost Management focuses on financial reporting, budgeting, and cost analysis. Azure Advisor provides personalized recommendations for performance, security, reliability, and cost. While Advisor includes cost suggestions, Cost Management offers deeper financial insights and control.
Mastering Azure Cost Management is no longer optional—it’s a business imperative. With cloud spending expected to exceed $1.5 trillion by 2026, every dollar saved through optimization directly impacts profitability. By leveraging native tools like Cost Analysis, Budgets, and Recommendations—and combining them with strategies like reservations, automation, and tagging—you can gain full control over your Azure spend. The key is consistency: regular monitoring, proactive optimization, and fostering a cost-aware culture across teams. As Azure evolves with AI-driven insights and sustainability features, the future of cost management will be smarter, faster, and more integrated than ever. Start today, and turn your cloud investment into a strategic advantage.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: