Azure Virtual Machines: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Welcome to the world of cloud computing, where flexibility meets performance. Azure Virtual Machines offer scalable, on-demand computing resources that empower businesses to innovate faster and smarter.
What Are Azure Virtual Machines?

Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) are Microsoft’s Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offering, allowing users to deploy and manage virtualized servers in the cloud. Unlike traditional physical servers, Azure VMs eliminate the need for hardware procurement, maintenance, and physical space, providing a fully scalable environment that adapts to your workload demands.
Understanding IaaS and Its Role
Infrastructure-as-a-Service is one of the foundational cloud service models, alongside Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). With IaaS, Microsoft manages the physical infrastructure—servers, storage, networking—while you retain control over operating systems, applications, and data.
- Full administrative access to the VM
- Choice of OS: Windows, Linux, or custom images
- Integration with other Azure services like networking and security
This model is ideal for organizations that want cloud agility without sacrificing control over their environments.
How Azure VMs Compare to Physical Servers
Traditional on-premises servers require significant capital investment, ongoing maintenance, and long deployment cycles. In contrast, Azure VMs can be provisioned in minutes, scaled up or down based on demand, and billed only for the compute time used.
- No upfront hardware costs
- Global availability across Microsoft’s data centers
- Automated backups and disaster recovery options
“Azure Virtual Machines give you the flexibility of virtualization without the cost and complexity of owning and managing physical hardware.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Azure Virtual Machines: Core Features and Capabilities
Azure VMs are packed with features that make them a top choice for enterprises, developers, and IT professionals. From flexible sizing to advanced networking, these capabilities ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Flexible VM Sizing and Series Options
Microsoft offers a wide range of VM sizes tailored to different workloads. These are grouped into series such as General Purpose, Compute Optimized, Memory Optimized, Storage Optimized, and GPU-Optimized.
- B-series: Budget-friendly, ideal for dev/test and low-traffic apps
- D-series: General-purpose with SSD storage, great for enterprise apps
- F-series: Compute-optimized for CPU-intensive tasks
- E-series: Memory-optimized for in-memory databases like SAP HANA
- Ls-series: High disk throughput for big data and data warehousing
- NC/ND-series: GPU-powered for AI, machine learning, and rendering
Each size comes with specific vCPU, memory, and storage configurations, allowing precise alignment with your application needs.
High Availability and Scalability
Azure ensures high availability through features like Availability Sets, Availability Zones, and Scale Sets.
- Availability Sets: Distribute VMs across fault and update domains to minimize downtime during host maintenance
- Availability Zones: Physically separate data centers within a region for zone-redundant deployments
- Virtual Machine Scale Sets: Automatically scale the number of VM instances based on demand, ideal for web apps and microservices
These features ensure your applications remain online and responsive, even during peak loads or infrastructure failures.
Deploying Azure Virtual Machines: Step-by-Step Guide
Getting started with Azure VMs is straightforward, whether you’re using the Azure portal, CLI, PowerShell, or ARM templates. This section walks you through the deployment process and best practices.
Creating a VM via the Azure Portal
The Azure portal provides a user-friendly interface for deploying VMs. Here’s how:
- Sign in to the Azure Portal
- Navigate to “Virtual Machines” and click “Create”
- Choose a subscription and resource group
- Select a region (e.g., East US, West Europe)
- Pick an image: Windows Server, Ubuntu, CentOS, or custom
- Choose a VM size based on performance needs
- Configure administrator credentials (username/password or SSH key)
- Set up networking (virtual network, subnet, public IP, NSG)
- Enable monitoring, backup, and auto-shutdown if needed
- Review and create
Within minutes, your VM will be up and running.
Automating Deployment with Azure CLI and PowerShell
For repeatable and scalable deployments, automation is key. Azure CLI and PowerShell allow script-based provisioning.
Example using Azure CLI:
az group create --name MyResourceGroup --location eastus
az vm create --resource-group MyResourceGroup --name MyVM --image UbuntuLTS --admin-username azureuser --generate-ssh-keysThis command creates a resource group and a Linux VM with SSH access. You can integrate this into CI/CD pipelines or DevOps workflows.
Using ARM Templates for Infrastructure as Code
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates are JSON-based definitions of your infrastructure. They enable consistent, version-controlled deployments.
- Define VMs, networks, disks, and security rules in a single file
- Deploy using Azure CLI, PowerShell, or Azure DevOps
- Support for parameters, variables, and conditions
ARM templates are essential for enterprise environments requiring compliance, auditability, and repeatability.
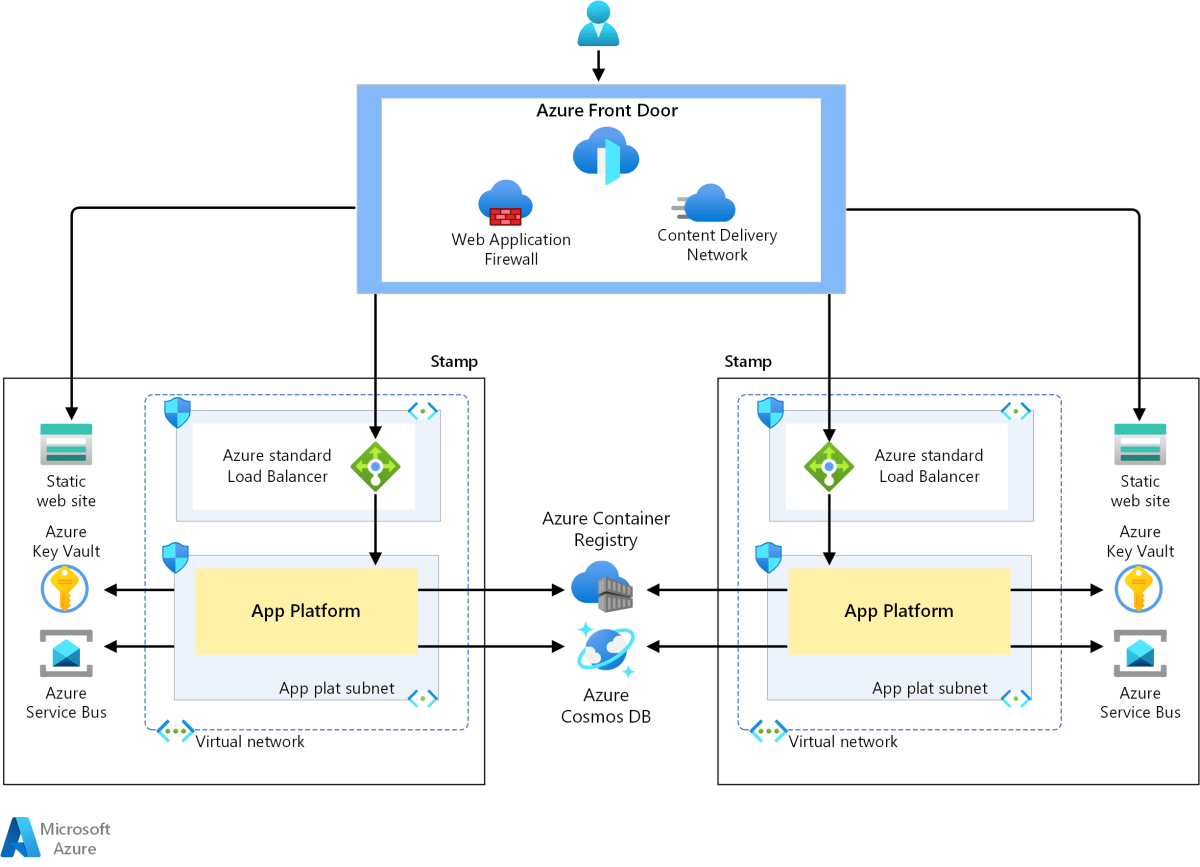
Networking and Security for Azure Virtual Machines
Secure and efficient networking is critical when running Azure Virtual Machines. Microsoft provides robust tools to manage connectivity, traffic flow, and protection.
Virtual Networks and Subnets
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is the fundamental building block for private networks in Azure. It enables isolation, segmentation, and secure communication between VMs.
- Create VNets to mimic on-premises network topologies
- Divide into subnets for different tiers (web, app, database)
- Assign private IP addresses from defined address spaces
- Enable DNS resolution and routing within the VNet
You can also connect VNets across regions using VNet peering or to on-premises networks via VPN Gateway or ExpressRoute.
Azure Virtual Machines – Azure Virtual Machines menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Network Security Groups (NSGs)
NSGs act as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic to VMs and subnets.
- Define rules based on source/destination IP, port, and protocol
- Allow or deny traffic (e.g., allow HTTP on port 80, block RDP from public internet)
- Apply NSGs at the subnet or NIC level
Best practice: Minimize exposure by restricting public access and using jump boxes or bastion hosts for administration.
Azure Bastion and Just-in-Time Access
To enhance security, Azure offers:
- Azure Bastion: A fully managed service that provides secure RDP/SSH access to VMs over SSL without exposing public IPs
- Just-in-Time (JIT) VM Access: Part of Microsoft Defender for Cloud, it locks down management ports and grants temporary access only when needed
These tools reduce the attack surface and prevent unauthorized access attempts.
Storage Options for Azure Virtual Machines
Storage is a critical component of Azure Virtual Machines, directly impacting performance, durability, and cost. Azure offers multiple disk types and storage configurations.
Managed Disks: Simplicity and Reliability
Azure Managed Disks simplify storage management by abstracting away storage accounts. You don’t need to worry about storage account limits or performance bottlenecks.
- Standard HDD: Cost-effective for dev/test and non-critical workloads
- Standard SSD: Balanced performance for production apps
- Premium SSD: High-performance, low-latency disks for I/O-intensive applications
- Ultra Disk: Highest performance with configurable IOPS and throughput, ideal for SAP, Oracle, and high-frequency trading systems
Managed disks are automatically replicated within the region for durability.
Unmanaged Disks and When to Use Them
Unmanaged disks require you to manage storage accounts manually. While largely deprecated in favor of managed disks, they may still be used in legacy systems or specific migration scenarios.
- Requires careful planning of storage account capacity
- Potential for performance throttling if multiple VMs share a storage account
- Not recommended for new deployments
Microsoft strongly encourages the use of managed disks for all new VMs.
Temporary vs. Persistent Storage
Azure VMs include temporary storage (usually on D: or /mnt) that resides on the host server.
- High-speed, ephemeral storage for temporary data (e.g., page files, caches)
- Data is lost during maintenance, reboot, or deallocation
- Not suitable for databases or critical files
Persistent storage (OS and data disks) is stored in Azure Storage and survives VM restarts.
Monitoring, Backup, and Disaster Recovery
Ensuring the health, availability, and recoverability of Azure Virtual Machines is essential for business continuity.
Monitoring with Azure Monitor and Log Analytics
Azure Monitor collects performance metrics, logs, and alerts from your VMs.
- Track CPU, memory, disk, and network usage
- Set up alerts for threshold breaches
- Use Log Analytics workspace to query and visualize logs
- Integrate with Application Insights for app-level monitoring
You can also install the Log Analytics agent or use Azure Monitor Agent (preview) for deeper insights.
Backup with Azure Backup Service
Azure Backup provides automated, encrypted backups for VMs.
- Create recovery points stored in Recovery Services vaults
- Supports both full and incremental backups
- Point-in-time restore capabilities
- Retention policies from days to years
Backups are stored in geo-redundant storage by default, ensuring protection against regional outages.
Disaster Recovery with Azure Site Recovery
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) enables replication of on-premises or Azure VMs to another region.
- Replicate VMs asynchronously to a secondary region
- Failover and failback with minimal data loss
- Test failover without impacting production
- Supports both VMware/physical servers and Azure VMs
ASR is critical for meeting RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) requirements.
Cost Management and Optimization for Azure Virtual Machines
While Azure VMs offer flexibility, costs can escalate without proper planning. Understanding pricing models and optimization strategies is crucial.
Understanding Azure VM Pricing Models
Azure offers several pricing options:
- Pay-As-You-Go: Pay by the second for running VMs
- Reserved Instances: Save up to 72% by committing to 1 or 3 years
- Spot VMs: Use unused capacity at up to 90% discount, ideal for fault-tolerant workloads
- Hybrid Benefit: Save on Windows Server licensing if you have existing on-premises licenses
Use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate costs before deployment.
Azure Virtual Machines – Azure Virtual Machines menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Right-Sizing and Auto-Shutdown
Many organizations over-provision VMs, leading to wasted spend.
- Use Azure Advisor to recommend optimal VM sizes
- Downsize underutilized VMs (e.g., from D4 to D2)
- Enable auto-shutdown for dev/test VMs outside business hours
- Use Azure Cost Management + Billing to track spending by resource, department, or tag
Scaling Strategies to Reduce Costs
Instead of running large VMs 24/7, consider:
- Using Scale Sets to add/remove instances based on load
- Combining Spot VMs with on-demand instances for batch processing
- Leveraging Azure Functions or containers for lightweight tasks
These strategies ensure you pay only for what you need.
Advanced Use Cases and Integrations
Azure Virtual Machines are not just for hosting websites. They power complex enterprise workloads and integrate seamlessly with other cloud services.
Running Enterprise Applications on Azure VMs
Many organizations migrate mission-critical applications to Azure VMs, including:
- SAP ERP and S/4HANA
- Oracle Database
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Active Directory and Domain Controllers
Azure provides certified configurations and support for these workloads, ensuring performance and compliance.
Hybrid Cloud with Azure Arc
Azure Arc extends Azure management to on-premises, multi-cloud, and edge environments.
- Manage VMs running outside Azure (e.g., AWS, GCP, on-prem) from the Azure portal
- Apply policies, deploy configurations, and monitor health centrally
- Enable consistent governance across environments
This is a game-changer for organizations with hybrid infrastructure.
AI and Machine Learning Workloads
Azure VMs with GPUs (NC, ND, NV series) are used for:
- Training deep learning models
- Image and speech recognition
- 3D rendering and video encoding
- High-performance computing (HPC)
These VMs integrate with Azure Machine Learning, Kubernetes, and NVIDIA frameworks.
What are Azure Virtual Machines used for?
Azure Virtual Machines are used to run a wide range of workloads in the cloud, including web servers, enterprise applications (like SAP or SQL Server), development and testing environments, big data processing, AI/ML training, and hybrid cloud scenarios. They provide full control over the operating system and applications, making them ideal for customizable and scalable computing needs.
How much do Azure VMs cost?
Costs vary based on VM size, region, OS, and usage. Prices range from a few dollars per month for B-series VMs to thousands for high-end GPU or memory-optimized instances. You can reduce costs using Reserved Instances (up to 72% savings), Spot VMs (up to 90% off), and Azure Hybrid Benefit. Use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate your costs.
How do I secure my Azure Virtual Machines?
Secure your VMs by using Network Security Groups (NSGs) to control traffic, enabling Azure Defender for threat detection, using Azure Bastion for secure RDP/SSH access, and applying Just-in-Time access. Also, keep the OS and applications patched, use strong authentication (SSH keys, MFA), and encrypt disks with Azure Disk Encryption.
Can I migrate on-premises servers to Azure VMs?
Yes, you can migrate physical or virtual servers to Azure using tools like Azure Migrate, which assesses your environment, replicates servers, and performs cutover with minimal downtime. Azure Site Recovery also supports continuous replication for disaster recovery and migration.
What is the difference between Azure VMs and Azure App Service?
Azure Virtual Machines give you full control over the OS and infrastructure (IaaS), while Azure App Service is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that hosts web apps without managing the underlying servers. Use VMs for custom or complex apps; use App Service for simpler, scalable web applications with less management overhead.
Azure Virtual Machines are a cornerstone of Microsoft’s cloud platform, offering unmatched flexibility, scalability, and integration. Whether you’re migrating legacy systems, building cloud-native apps, or running AI workloads, Azure VMs provide the infrastructure you need. By leveraging features like managed disks, auto-scaling, security tools, and cost optimization strategies, organizations can achieve high performance and reliability while controlling expenses. As cloud adoption grows, mastering Azure Virtual Machines becomes essential for IT professionals and developers alike.
Azure Virtual Machines – Azure Virtual Machines menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: